Using ETFs for stock market strategies introduces a powerful tool for investors looking to optimize their returns in the stock market. From understanding the basics to implementing advanced trading techniques, this guide covers everything you need to know about leveraging ETFs for success.
Exploring the different types of ETFs, selection criteria, and trading strategies, this comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial markets with confidence.
Introduction to ETFs

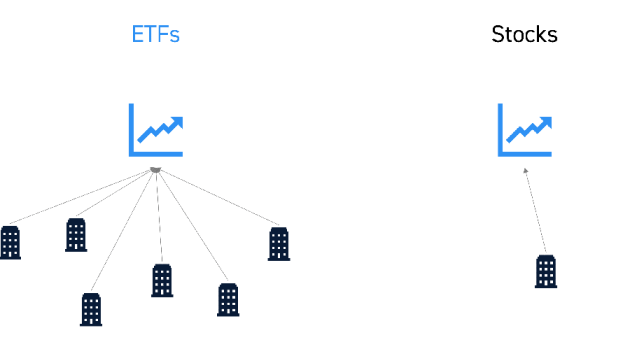
ETFs, or Exchange-Traded Funds, are investment funds that are traded on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks. However, they differ in that they hold assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, providing investors with diversified exposure to a specific market or sector in a single investment.
ETFs offer several benefits for stock market strategies. They provide instant diversification by holding a basket of securities, reducing individual stock risk. Additionally, they offer liquidity, as they can be bought and sold throughout the trading day. Moreover, ETFs often have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them a cost-effective investment option.
Some popular ETFs commonly used for investment purposes include SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY), which tracks the performance of the S&P 500 Index, and Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ), which follows the Nasdaq-100 Index. Other examples include Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI) and iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM), providing exposure to different asset classes and regions for investors.
Types of ETFs
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) come in various types, each with its own unique characteristics and investment objectives. Understanding the different types can help investors make informed decisions when building their portfolios.
Equity ETFs
Equity ETFs invest primarily in stocks and aim to track a specific stock market index, sector, or industry. These ETFs offer diversification across a wide range of companies within a particular market segment.
When it comes to investing, high-growth stocks are often sought after for long-term gains. These stocks have the potential to outperform the market and provide significant returns over time. By focusing on companies with strong growth prospects and solid financials, investors can position themselves for success in the long run.
To learn more about high-growth stocks and how they can benefit your investment portfolio, check out this detailed guide on high-growth stocks for long-term gains.
Bond ETFs
Bond ETFs invest in fixed-income securities such as government, corporate, or municipal bonds. They provide investors with exposure to the bond market while offering diversification and potentially higher yields compared to individual bonds.
When it comes to investing, high-growth stocks are often sought after for long-term gains. These stocks have the potential to outperform the market and deliver significant returns over time. However, it’s important to do thorough research and analysis before diving in.
Understanding the company’s financials, market trends, and growth prospects is essential for making informed investment decisions. Check out this article on high-growth stocks for long-term gains to learn more about how to identify and invest in these promising opportunities.
Commodity ETFs
Commodity ETFs track the performance of commodities such as gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products. Investors can gain exposure to the commodity market without physically owning the underlying assets. These ETFs can serve as a hedge against inflation or provide portfolio diversification.
Advantages and Disadvantages, Using ETFs for stock market strategies
- Advantages:
- ETFs offer diversification within a single investment.
- They are traded on exchanges, providing liquidity and transparency.
- ETFs typically have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
- Investors can buy and sell ETFs throughout the trading day at market prices.
- Disadvantages:
- ETF prices can be subject to market volatility and may deviate from the net asset value (NAV).
- Some ETFs may have lower trading volumes, leading to wider bid-ask spreads.
- Not all ETFs are tax-efficient, potentially leading to higher tax liabilities for investors.
ETF Selection Criteria

When selecting ETFs for stock market strategies, it is crucial to consider various factors that can impact the performance and suitability of the investment. Factors such as expense ratio, liquidity, tracking error, and underlying assets play a significant role in determining the most appropriate ETFs for a specific investment goal.
Expense Ratio
The expense ratio of an ETF is the annual fee charged by the fund to cover operating expenses. A lower expense ratio is generally preferable as it reduces the overall cost of holding the ETF. Investors should compare expense ratios across similar ETFs to ensure they are getting the best value for their investment.
Liquidity
Liquidity refers to how easily an ETF can be bought or sold in the market without significantly impacting its price. High liquidity is important for efficient trading and helps investors enter and exit positions with minimal slippage. It is advisable to choose ETFs with sufficient trading volume to ensure liquidity.
Tracking Error
Tracking error measures the divergence between an ETF’s performance and the performance of its underlying index. A lower tracking error indicates that the ETF closely follows its benchmark index. Investors should evaluate the historical tracking error of an ETF to assess its ability to replicate the index accurately.
Step-by-Step Guide to Evaluate and Choose ETFs
- Identify Investment Goals: Determine your investment objectives and risk tolerance to narrow down the selection criteria.
- Research ETF Options: Conduct thorough research on different ETFs that align with your investment goals and compare their attributes.
- Assess Expense Ratios: Compare the expense ratios of shortlisted ETFs to identify cost-effective options.
- Evaluate Liquidity: Look at the average trading volume and bid-ask spreads of ETFs to ensure adequate liquidity.
- Analyze Tracking Error: Review the historical tracking error of ETFs to gauge their ability to track the underlying index accurately.
- Diversify Portfolio: Select a combination of ETFs from various asset classes to achieve diversification and minimize risk.
Tips on Diversifying a Portfolio
Diversification is key to managing risk and optimizing returns in an investment portfolio. By combining ETFs from different sectors, regions, and asset classes, investors can spread risk and capture opportunities across various market segments. It is essential to maintain a balanced allocation and periodically rebalance the portfolio to ensure it aligns with changing market conditions.
ETF Trading and Market Strategies

Investors can utilize ETFs to implement various stock market strategies that suit their investment goals and risk tolerance. Whether it’s a long-term buy-and-hold approach, sector rotation strategy, or tactical asset allocation, ETFs offer a flexible and cost-effective way to gain exposure to different market segments.
Role of ETFs in Hedging and Risk Management
ETFs play a crucial role in hedging against market volatility and managing risk in a portfolio. By holding a diversified basket of securities within a single ETF, investors can reduce the impact of individual stock price fluctuations, thereby mitigating overall portfolio risk. Additionally, inverse ETFs or leveraged ETFs can be used to hedge against specific market movements, providing downside protection in turbulent times.
Successful ETF Trading Strategies
- Market Conditions: In bullish market conditions, investors may opt for a buy-and-hold strategy with broad market ETFs like S&P 500 ETFs to capture overall market growth. Conversely, during bearish markets, defensive sector ETFs like utilities or consumer staples can provide stability.
- Sector Rotation: ETFs allow investors to rotate their exposure across different sectors based on economic cycles. For example, during an economic recovery, cyclical sector ETFs like industrials or materials may outperform defensive sectors like healthcare or utilities.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: Investors can dynamically adjust their asset allocation using ETFs to capitalize on short-term market opportunities or manage downside risk. By rebalancing their ETF holdings based on market conditions, investors can optimize returns and minimize losses.
Closing Summary: Using ETFs For Stock Market Strategies
In conclusion, Using ETFs for stock market strategies offers a roadmap to enhance your investment portfolio and achieve your financial goals. By harnessing the potential of ETFs, investors can diversify their holdings, manage risk effectively, and capitalize on market opportunities with precision. Stay informed, stay strategic, and let ETFs be your gateway to a prosperous investment journey.