Swing trading strategies for stocks take the spotlight as we delve into the world of stock market trading tactics, offering readers a comprehensive guide filled with valuable insights and practical tips for success.
Exploring the nuances of technical analysis tools, setting entry and exit points, and implementing risk management strategies, this article equips traders with the knowledge needed to thrive in the dynamic world of swing trading.
Overview of Swing Trading Strategies for Stocks

Swing trading in the stock market involves holding positions for a few days to weeks to take advantage of short- to medium-term price movements. This strategy aims to capture gains from a stock’s ‘swing’ in price, typically caused by market fluctuations or news events.
Having a well-defined strategy for swing trading is crucial for success in this volatile market. It helps traders to set clear entry and exit points, manage risk effectively, and stay disciplined in their approach. Without a solid plan, traders may fall prey to impulsive decisions or emotional trading, leading to losses.
Importance of Having a Well-Defined Strategy
- Setting clear entry and exit points: A defined strategy helps traders identify optimal points to enter and exit trades, maximizing profit potential.
- Managing risk: By outlining risk management rules, traders can protect their capital and avoid catastrophic losses.
- Staying disciplined: Following a well-defined strategy helps traders avoid emotional decision-making and stick to their plan, even during turbulent market conditions.
Benefits of Swing Trading
- Flexibility: Swing trading allows traders to capitalize on short- to medium-term price movements without the need to monitor positions constantly.
- Lower time commitment: Compared to day trading, swing trading requires less time and allows traders to maintain other commitments alongside their trading activities.
- Potential for higher returns: By capturing the ‘swings’ in stock prices, swing traders have the opportunity to generate significant profits in a relatively short period.
Technical Analysis Tools for Swing Trading

Swing traders rely on a variety of technical analysis tools to identify potential entry and exit points for trades. These tools help traders analyze price movements and make informed decisions based on market trends.
Moving Averages
Moving averages are one of the most commonly used technical indicators in swing trading. Traders use moving averages to smooth out price data and identify trends over a specific period. The two main types of moving averages are the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). The SMA gives equal weight to all data points, while the EMA gives more weight to recent data. By analyzing the crossover of different moving averages, traders can identify potential entry and exit points for trades.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is another popular technical indicator used in swing trading. The RSI measures the speed and change of price movements and helps traders determine if a stock is overbought or oversold. A reading above 70 indicates that a stock may be overbought, while a reading below 30 indicates that a stock may be oversold. By using the RSI in conjunction with other technical tools, traders can confirm potential entry and exit points for trades.
Combining Tools for Effective Swing Trading
To enhance their swing trading strategies, traders often combine different technical analysis tools. For example, a trader may use moving averages to identify the overall trend of a stock and the RSI to confirm potential entry and exit points within that trend. By combining multiple tools, traders can reduce the risk of false signals and make more informed trading decisions.
Setting Entry and Exit Points
Setting entry and exit points is a crucial aspect of swing trading strategies for stocks. It involves identifying the optimal points to enter a trade and exit it to maximize profits and minimize losses.
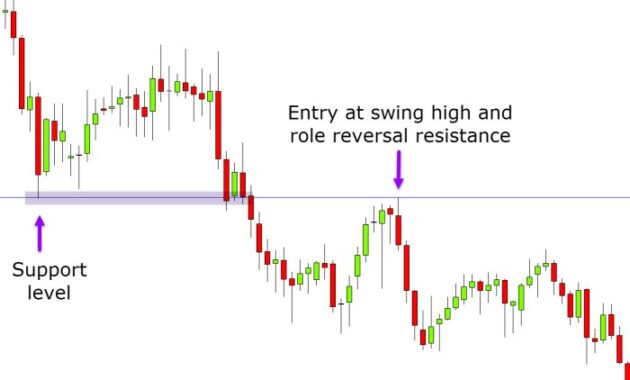
Significance of Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance levels play a key role in determining entry and exit points for swing trades. Support levels indicate a price level where a stock tends to stop falling and bounce back, while resistance levels represent a price level where a stock tends to stop rising and pull back. Traders often use these levels to identify potential entry points near support levels and exit points near resistance levels.
- When setting entry points, traders may look for stocks that are approaching a support level, as this could indicate a potential buying opportunity with less downside risk.
- For exit points, traders may consider selling near a resistance level, as the stock price may struggle to break through that level and could reverse its trend.
- By using support and resistance levels, traders can establish a clear plan for their trades and have predefined points to enter and exit positions.
Tips to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Avoid chasing stocks that have already made significant moves, as they may be nearing resistance levels and could reverse their trend.
- Set stop-loss orders to protect against potential losses if the trade moves against you, based on the support levels identified.
- Consider using technical indicators like moving averages or MACD to confirm entry and exit points based on the stock’s momentum and trend.
- Regularly review and adjust your entry and exit points based on new information or changes in market conditions to adapt to the evolving stock price movements.
Risk Management Strategies for Swing Trading: Swing Trading Strategies For Stocks

When it comes to swing trading, risk management is crucial for protecting capital and maximizing profits. By implementing effective risk management strategies, traders can mitigate potential losses and increase their chances of success in the market.
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
One of the key risk management techniques for swing traders is setting stop-loss orders. A stop-loss order is a predetermined price level at which a trader will exit a trade to limit losses. By setting stop-loss orders, traders can protect their capital from significant declines in stock prices.
Position Sizing and Risk-Reward Ratios, Swing trading strategies for stocks
Position sizing and risk-reward ratios are essential aspects of risk management in swing trading. Position sizing refers to the amount of capital allocated to each trade, while risk-reward ratios assess the potential return relative to the risk taken. By carefully managing position sizes and maintaining favorable risk-reward ratios, traders can optimize their trading performance.
Protecting Capital and Maximizing Profits
Effective risk management strategies can help traders protect their capital during adverse market conditions and capitalize on profitable opportunities. For example, by setting tight stop-loss orders and maintaining favorable risk-reward ratios, traders can minimize losses and maximize profits over time. Additionally, disciplined risk management can instill confidence and consistency in trading decisions, leading to long-term success in swing trading.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering swing trading strategies for stocks requires a combination of skill, discipline, and a deep understanding of the market. By implementing the techniques discussed here, traders can enhance their profitability and navigate the stock market with confidence.
When it comes to diversifying your investment portfolio, considering international stocks is essential. By adding international stocks to your portfolio, you can reduce risk and potentially increase returns. You can learn more about the benefits of diversifying with international stocks here.
When it comes to diversifying your investment portfolio, considering international stocks for diversification is essential. Investing in companies outside your home country can help spread risk and potentially increase returns. By including international stocks in your portfolio, you can take advantage of different market cycles and economic conditions around the world.
This strategy can provide a level of protection against regional downturns and enhance overall portfolio performance.