Maker (MKR) token use cases are at the forefront of decentralized finance (DeFi), revolutionizing the way we interact with cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Dive into the world of Maker (MKR) tokens as we explore their multifaceted applications and impact on the digital economy.
As we delve deeper, you’ll uncover the intricate web of functionalities that make Maker (MKR) tokens a crucial component in the realm of decentralized finance, setting a new standard for innovation and financial empowerment.
Introduction to Maker (MKR) token
Maker (MKR) token plays a crucial role within the cryptocurrency ecosystem, particularly in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. It is the governance token of the MakerDAO platform, which operates on the Ethereum blockchain. MKR token holders have the power to vote on key decisions that impact the platform, such as changes to stability fees and collateral types.
Unique Features of Maker (MKR) token
- Decentralized Governance: MKR token holders have voting rights to make decisions on proposals within the MakerDAO ecosystem, ensuring a decentralized and community-driven approach.
- Stability Mechanism: MKR token is used to stabilize the value of the stablecoin DAI, acting as a backstop in times of market volatility to maintain the peg to the US dollar.
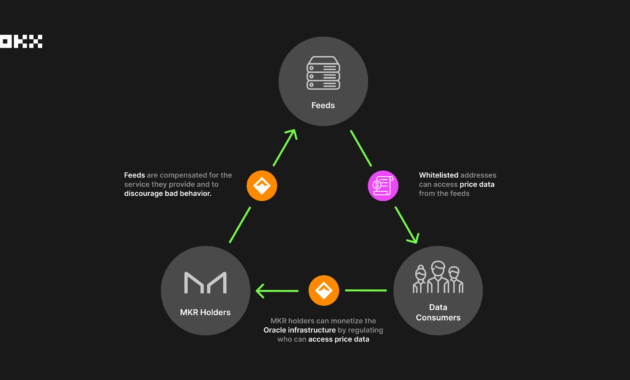
- Collateralization: MKR tokens are also used as collateral within the MakerDAO platform, providing a source of liquidity and stability for the system.
Governance and Voting Rights

Maker (MKR) token holders play a crucial role in the governance of the MakerDAO platform, where they have the power to vote on important decisions that impact the ecosystem.
Participation in Governance
- Maker (MKR) token holders can participate in governance by staking their tokens in the voting system.
- They have the ability to propose and vote on changes to the platform, including adjustments to collateral types, stability fees, and other parameters.
- Decisions are made through a continuous approval voting system, where proposals need to reach a certain approval threshold to be implemented.
Voting Mechanisms
- Maker (MKR) token holders can cast their votes directly or delegate their voting power to representatives.
- Voting power is proportional to the amount of MKR tokens held, giving larger holders more influence over decisions.
- There is a cooling-off period after each vote to allow for deliberation and prevent rushed decisions.
Significant Governance Decisions, Maker (MKR) token use cases
- One of the significant governance decisions made by Maker (MKR) token holders was the introduction of new collateral types to diversify the assets backing the stablecoin DAI.
- Another example is the adjustment of stability fees to maintain the peg of DAI to the US dollar during periods of high volatility in the market.
- Maker (MKR) token holders have also voted on changes to the governance structure itself, aiming to improve transparency and efficiency in decision-making processes.
Stability Fees and Collateralization
Stability fees and collateralization are crucial components within the MakerDAO ecosystem, impacting the stability of the DAI stablecoin and the overall health of the decentralized finance (DeFi) system.
Maker (MKR) token plays a vital role in setting stability fees within the MakerDAO ecosystem. Stability fees are essentially interest rates that borrowers pay when they generate DAI by locking up their collateral in the MakerDAO system. MKR token holders have the power to vote on and adjust these stability fees based on market conditions and risk assessments. By increasing or decreasing stability fees, MKR token holders can influence the supply and demand of DAI to maintain its peg to the US dollar.
Collateralization for DAI Issuance
Collateralization is the process of locking up assets to generate DAI stablecoin within the MakerDAO system. MKR token holders can use their MKR tokens as collateral to issue DAI. However, it’s important to note that MKR tokens are considered a risky form of collateral due to their price volatility. As a result, a higher collateralization ratio is required for MKR tokens compared to other assets within the system.
Comparison of Collateralization Requirements
- ETH: Ether (ETH) is one of the most commonly used assets as collateral within the MakerDAO system. It has a lower collateralization ratio compared to MKR tokens due to its relatively lower price volatility and higher liquidity.
- WBTC: Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is another popular collateral option within MakerDAO. It also has a lower collateralization ratio compared to MKR tokens, similar to ETH.
- Other Tokens: For assets with higher price volatility or lower liquidity, such as MKR tokens, a higher collateralization ratio is required to mitigate the risk of liquidation and maintain the stability of the DAI stablecoin.
Risk Management and Liquidation: Maker (MKR) Token Use Cases

When it comes to managing risks and ensuring the stability of the DAI stablecoin, the role of Maker (MKR) token is crucial. Maker (MKR) token holders play a significant part in the risk management and liquidation process within the MakerDAO ecosystem.
Risk Management with Maker (MKR) Token
- Maker (MKR) token holders serve as the governance body that votes on proposed changes to the system, including adjustments to stability fees and collateralization ratios.
- Through their voting rights, MKR holders can make decisions that impact the risk exposure of the MakerDAO system, helping to maintain the stability of DAI.
- The Maker (MKR) token acts as a form of insurance for the system, as MKR holders are financially responsible in case the system faces insolvency or needs emergency funds.
Liquidation Process and Involvement of MKR Holders
- When a vault’s collateral falls below the required collateralization ratio, it becomes eligible for liquidation to cover the outstanding DAI debt and stability fees.
- Maker (MKR) token holders participate in the liquidation process by triggering auctions to sell off the collateral at a discount to repay the outstanding debt and stabilize the system.
- Through these auctions, MKR holders help mitigate the risk of under-collateralization and ensure the solvency of the MakerDAO ecosystem.
Mechanisms Ensuring Stability of Maker (MKR) Token Ecosystem
- The stability fee, which is paid in DAI by borrowers, helps regulate the demand for borrowing and maintains the peg of DAI to the US dollar.
- Collateralization ratios set the minimum amount of collateral required for each vault, reducing the risk of liquidation and ensuring the system’s stability.
- The continuous governance and monitoring by MKR token holders provide a decentralized approach to managing risks and maintaining the resilience of the MakerDAO platform.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, Maker (MKR) token use cases exemplify the transformative power of blockchain technology, reshaping traditional financial systems and paving the way for a more inclusive and efficient future. Embrace the possibilities that Maker (MKR) tokens offer and embark on a journey towards a decentralized financial landscape that is both dynamic and accessible to all.
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that are designed to have a stable value, often pegged to a reserve asset like the US dollar. They offer a solution to the extreme price volatility that is common in the cryptocurrency market.
To understand more about stablecoins, you can read this detailed guide on What is a stablecoin?.
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency that is pegged to a stable asset, such as a fiat currency like the US dollar or commodities like gold. This stability is achieved by maintaining reserves equal to the circulating supply of the stablecoin.
To learn more about what stablecoins are and how they work, check out this comprehensive guide on What is a stablecoin?.