Investing in growth vs. value stocks opens up a world of possibilities for investors seeking to navigate the complex landscape of the stock market. Delve into the nuances of these two investment strategies and discover which path may lead to greater financial success.
Growth Stocks vs. Value Stocks: Investing In Growth Vs. Value Stocks
When it comes to investing in the stock market, two common strategies that investors often consider are growth stocks and value stocks. Understanding the key differences between these two types of stocks can help investors make informed decisions about where to allocate their funds.
Characteristics of Growth Stocks
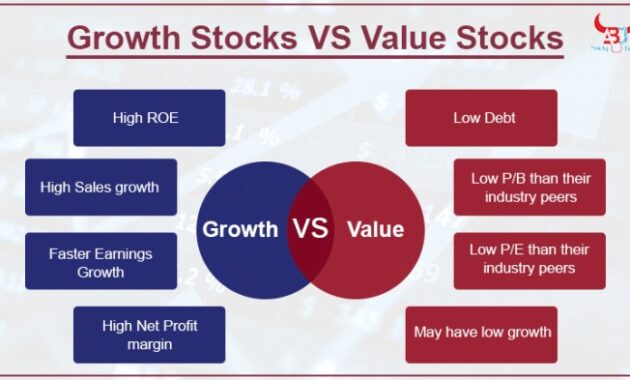
Growth stocks are shares of companies that are expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to other companies in the market. These companies typically reinvest their earnings back into the business to fuel expansion, rather than paying out dividends to shareholders. Characteristics of growth stocks include:
- High price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios
- Rapid revenue and earnings growth
- High volatility and risk
- Minimal dividends
Characteristics of Value Stocks
On the other hand, value stocks are shares of companies that are considered undervalued by the market. These companies are often more established with stable earnings and lower growth rates. Characteristics of value stocks include:
- Low price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios
- Steady dividend payments
- Lower volatility and risk
- Potential for price appreciation as the market corrects its undervaluation
Performance of Growth Stocks vs. Value Stocks
Historically, growth stocks have outperformed value stocks during bull markets when investor sentiment is positive, and economic conditions are favorable for companies with high growth potential. However, during periods of market downturns or economic uncertainties, value stocks have shown resilience and tend to outperform growth stocks due to their stable earnings and lower valuation.
Overall, the choice between investing in growth or value stocks depends on an investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and market conditions. Diversifying a portfolio with a mix of both growth and value stocks can help mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities in different market environments.
Investing Strategy

When it comes to investing in stocks, choosing between growth and value stocks is a crucial decision that can greatly impact your investment portfolio. Each strategy comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, as well as unique characteristics that appeal to different types of investors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Investing in Growth Stocks
- Growth stocks have the potential for high returns, as they typically experience rapid earnings and revenue growth.
- Investors in growth stocks are often attracted to innovative companies with promising future prospects.
- On the downside, growth stocks can be volatile and risky, as their valuations are often based on future potential rather than current earnings.
- During market downturns, growth stocks may experience sharper declines due to their higher valuation multiples.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Investing in Value Stocks
- Value stocks are usually more stable and less volatile, making them a safer investment option for conservative investors.
- These stocks are often undervalued by the market, offering the potential for significant price appreciation as their true value is recognized.
- However, value stocks may underperform during bull markets, as they are typically companies with slower growth rates.
- Investors in value stocks need to be patient and willing to wait for the market to appreciate the underlying value of the stock.
Successful Companies Considered Growth Stocks
- Amazon: Known for its continuous innovation and expansion into new markets, Amazon is a prime example of a growth stock.
- Tesla: The electric vehicle pioneer has seen exponential growth in recent years, positioning itself as a leader in the industry.
Examples of Companies Considered Value Stocks
- Johnson & Johnson: A well-established company with a history of stable earnings and dividends, Johnson & Johnson is often classified as a value stock.
- Exxon Mobil: Despite facing challenges in the energy sector, Exxon Mobil is considered a value stock due to its strong balance sheet and dividend yield.
Risk Assessment
When it comes to investing in growth and value stocks, understanding the associated risks is crucial for making informed decisions. Both types of stocks come with their own set of risks that investors need to consider before diving into the market.
Risks of Investing in Growth Stocks
- Growth stocks are often more volatile and susceptible to market fluctuations due to their high valuation based on future growth potential.
- There is a higher risk of price corrections or pullbacks, as investors may have already priced in the expected growth, leaving little room for error.
- Companies with high growth potential may also face challenges in meeting market expectations, leading to sharp declines in stock prices.
- Investing in growth stocks requires a longer time horizon, as it may take time for the growth to materialize and reflect in the stock price.
Risks of Investing in Value Stocks
- Value stocks are often undervalued due to market sentiment or temporary setbacks, which can lead to prolonged periods of underperformance.
- There is a risk of value traps, where stocks appear cheap but continue to decline in value without any significant improvement in fundamentals.
- Value investing requires patience and discipline, as it may take time for the market to recognize the true value of the stock.
- Value stocks may also be more exposed to economic downturns or industry-specific challenges, impacting their performance.
Comparison of Risk Levels, Investing in growth vs. value stocks
- Growth stocks typically have higher risk levels due to their volatile nature and dependence on future growth expectations.
- Value stocks, while less volatile, come with their own set of risks related to undervaluation and potential value traps.
- Investors need to assess their risk tolerance and investment goals when choosing between growth and value stocks to create a balanced portfolio.
Market Conditions
Market conditions play a crucial role in influencing the performance of both growth and value stocks. Understanding how economic factors can impact these two types of stocks is essential for investors looking to navigate the stock market effectively.
Impact on Growth Stocks
Market conditions can greatly affect the performance of growth stocks. During periods of economic expansion and optimism, growth stocks tend to outperform value stocks. This is because investors are more willing to take on risk and invest in companies with high growth potential. On the other hand, during economic downturns or periods of uncertainty, growth stocks may underperform as investors become more risk-averse and shift towards safer investments.
Impact on Value Stocks
Value stocks, on the other hand, are often more resilient during economic downturns. When market conditions are unfavorable, value stocks may outperform growth stocks as investors seek out undervalued companies with stable cash flows and solid fundamentals. Value stocks are typically less volatile and can provide a buffer during turbulent times in the market.
Economic Factors and Their Differential Impact
Various economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth can affect growth and value stocks differently. For example, rising interest rates may negatively impact growth stocks, as they rely heavily on borrowing to fuel their expansion. On the other hand, value stocks may benefit from higher interest rates as they often have lower levels of debt and more stable cash flows.
Inflation can also have varying effects on growth and value stocks. High inflation may erode the future earnings potential of growth stocks, making them less attractive to investors. Value stocks, on the other hand, may be better positioned to weather inflationary pressures due to their focus on tangible assets and stable cash flows.
Overall, understanding how market conditions and economic factors can impact growth and value stocks differently is essential for investors looking to build a diversified and resilient portfolio.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investing

When it comes to investing in growth versus value stocks, one of the key considerations is the time horizon for your investment strategy. Let’s delve into whether growth stocks are more suitable for long-term or short-term investing, the viability of value stocks for long-term investment strategies, and compare the potential returns of long-term investing in growth versus value stocks.
Growth Stocks for Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investing
- Growth stocks are often seen as more suitable for long-term investing due to their potential for significant capital appreciation over time.
- Investors who opt for growth stocks typically have a longer investment horizon, allowing them to ride out market fluctuations and benefit from the compounding effect over the years.
- Short-term investing in growth stocks can be riskier due to the volatility associated with high-growth companies, making it more suitable for experienced investors or those with a high-risk tolerance.
Value Stocks for Long-Term Investment Strategies
- Value stocks, on the other hand, are often considered ideal for long-term investment strategies as they are undervalued by the market and have the potential for price appreciation as the market corrects its valuation.
- Investing in value stocks with a long-term perspective allows investors to benefit from the intrinsic value of the company, which may take time to be recognized by the market.
- Long-term investors in value stocks may also enjoy dividends as these companies tend to be more established and have a history of distributing profits to shareholders.
Potential Returns of Long-Term Investing in Growth vs. Value Stocks
- When it comes to potential returns, long-term investing in growth stocks can offer higher returns compared to value stocks, but with increased volatility and risk.
- Value stocks, while potentially offering more stable returns over the long run, may not provide the same level of growth as growth stocks during periods of economic expansion.
- Ultimately, the decision between investing in growth or value stocks for the long term will depend on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and financial situation.
Last Word

In conclusion, understanding the dynamics between growth and value stocks is crucial for making informed investment decisions. By weighing the pros and cons of each strategy, investors can tailor their portfolios to align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
When it comes to investing, one of the key decisions is whether to focus on small-cap or large-cap stocks. Small-cap stocks are known for their potential growth opportunities, while large-cap stocks offer stability and lower risk. Understanding the differences between the two can help investors make informed decisions.
To learn more about the comparison between small-cap and large-cap stocks, check out this comprehensive guide on Small-cap vs large-cap stocks.
When it comes to investing, one of the key decisions is choosing between small-cap and large-cap stocks. Small-cap stocks belong to companies with a market capitalization typically under $2 billion, offering potential for high growth but also higher risk. On the other hand, large-cap stocks are from established companies with market capitalization over $10 billion, providing stability and dividends.
Understanding the differences between small-cap and large-cap stocks is crucial for building a diversified portfolio.