Delving into Forex risk management strategies, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a focus on understanding the importance of implementing risk management strategies in the Forex trading world.
In this article, we will explore the various types of risks associated with Forex trading, common risk management techniques used by traders, and the significance of stop-loss orders and position sizing in managing risk effectively.
Definition of Forex Risk Management
Forex risk management refers to the process of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating the potential risks associated with trading currencies in the foreign exchange market. It involves implementing strategies to protect investments and minimize losses that may arise from market volatility and unexpected events.
Importance of Implementing Risk Management Strategies in Forex Trading
Effective risk management is crucial in Forex trading to safeguard capital and ensure long-term profitability. Without proper risk management, traders are susceptible to significant financial losses that can wipe out their accounts. By implementing risk management strategies, traders can protect themselves from adverse market conditions and maintain a sustainable trading portfolio.
- Setting Stop Loss Orders: Traders can use stop loss orders to automatically exit a trade when a certain price level is reached, limiting potential losses.
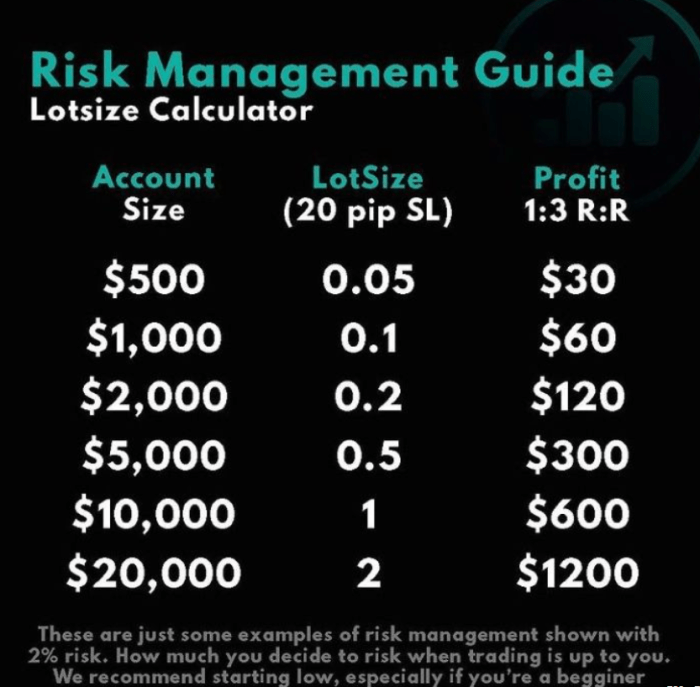
- Position Sizing: Determining the appropriate position size based on risk tolerance and account size helps control the amount of capital at risk in each trade.
- Diversification: Spreading out investments across different currency pairs and asset classes can reduce overall risk exposure in the Forex market.
- Risk-reward Ratio: Calculating the risk-reward ratio before entering a trade helps traders assess the potential profit against the amount at risk.
Types of Forex Risk

When engaging in Forex trading, it is important to be aware of the various types of risks that can impact your investments. These risks can come from different sources and have unique characteristics that traders need to consider in their risk management strategies.
Market Risk
Market risk refers to the potential for losses due to unfavorable movements in the overall market. This type of risk can arise from factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. For example, a sudden change in interest rates by a central bank can lead to market volatility, affecting currency prices and causing losses for traders.
Exchange Rate Risk
Exchange rate risk arises from fluctuations in currency values. When trading Forex, investors are exposed to the risk of exchange rate movements impacting the value of their investments. For instance, if a trader buys a currency pair and the exchange rate depreciates, they may experience losses when closing their position at a lower rate.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is linked to changes in interest rates set by central banks. Forex traders need to consider how shifts in interest rates can affect currency values and trading positions. For example, a decision to increase interest rates can strengthen a currency, while a rate cut may lead to depreciation. Traders must be prepared to adjust their strategies accordingly to manage interest rate risk effectively.
By understanding and distinguishing between these different types of risks, Forex traders can develop comprehensive risk management strategies to protect their investments and navigate the dynamic nature of the currency markets.
Common Forex Risk Management Strategies

When trading in the Forex market, it is crucial to have effective risk management strategies in place to protect your investments. There are several popular risk management techniques used by Forex traders to minimize potential losses and maximize profits. Let’s explore some of these strategies, along with their pros and cons and real-world examples of successful implementation.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are one of the most common risk management tools used by Forex traders. This strategy involves setting a predetermined price level at which a trade will be automatically closed to prevent further losses. The main advantage of stop-loss orders is that they help traders limit their losses and protect their capital. However, a potential downside is that stop-loss orders can sometimes be triggered by short-term price fluctuations, leading to premature exits from profitable trades.
Hedging
Hedging is another popular risk management technique that involves opening additional positions to offset potential losses in existing trades. By taking opposite positions in correlated assets, traders can protect themselves against adverse market movements. The benefit of hedging is that it can help traders reduce their overall risk exposure. On the other hand, hedging can also limit potential profits if both positions move in the same direction.
Position Sizing
Position sizing is a risk management strategy that involves determining the amount of capital to risk on each trade based on factors such as account size, risk tolerance, and market conditions. By carefully managing the size of each position, traders can control their overall risk exposure and protect their investments. The advantage of position sizing is that it allows traders to adjust their risk levels according to market volatility. However, a disadvantage is that overly conservative position sizing can limit potential profits.
These are just a few of the common Forex risk management strategies used by traders to navigate the unpredictable nature of the market. By implementing these techniques effectively and adapting them to suit their trading style, traders can improve their chances of success and safeguard their investments.
Importance of Stop-Loss Orders

Stop-loss orders play a crucial role in Forex risk management by helping traders limit potential losses in volatile markets.
When it comes to GBP/JPY trading, it’s crucial to have a solid strategy in place. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned trader, these GBP/JPY trading tips can help you navigate the market with confidence. From setting stop-loss orders to analyzing key market indicators, incorporating these tips into your trading routine can make a significant difference in your overall success.
Stay informed, stay disciplined, and always be prepared to adapt to changing market conditions.
Role of Stop-Loss Orders, Forex risk management strategies
Stop-loss orders are predetermined price levels set by traders to automatically close a trade position when the market moves against them. By doing so, traders can protect their capital and manage risk effectively.
When it comes to trading GBP/JPY, it’s essential to have a solid strategy in place. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, these GBP/JPY trading tips can help you navigate the market more effectively. From understanding the correlation between the two currencies to setting stop-loss orders, these tips cover a range of important aspects to consider in your trading journey.
Benefits of Stop-Loss Orders
- Preventing emotional decision-making: Stop-loss orders remove the need for impulsive decisions during market fluctuations, ensuring a disciplined approach to trading.
- Limiting losses: Setting stop-loss levels helps traders define the maximum amount they are willing to lose on a trade, preventing catastrophic losses.
- Enhancing risk management: By incorporating stop-loss orders into their trading strategy, traders can maintain a structured approach to risk management and protect their investment capital.
Setting Effective Stop-Loss Levels
When setting stop-loss levels, traders should consider factors such as market volatility, support and resistance levels, and their risk tolerance. Here are some tips for setting effective stop-loss levels:
- Use technical analysis: Identify key support and resistance levels on price charts to determine appropriate stop-loss levels.
- Consider volatility: Adjust stop-loss levels based on the volatility of the currency pair being traded to account for potential price fluctuations.
- Factor in risk-reward ratio: Ensure that the distance between the entry point and the stop-loss level aligns with the desired risk-reward ratio for the trade.
- Regularly review and adjust: Monitor market conditions and adjust stop-loss levels accordingly to reflect changes in price action and volatility.
Position Sizing Techniques
Position sizing is a crucial aspect of Forex risk management that helps traders control the amount of capital at risk in each trade. By determining the appropriate position size, traders can effectively manage risk and protect their trading accounts.
Fixed Percentage Method
- The fixed percentage method involves risking a set percentage of your trading account on each trade.
- For example, if you decide to risk 2% of your account on a trade and your account balance is $10,000, you would risk $200 on that trade.
- This method helps ensure consistency in risk management regardless of the size of your trading account.
Volatility-Based Position Sizing
- This method involves adjusting your position size based on the volatility of the currency pair you are trading.
- Higher volatility may require a smaller position size to account for larger price fluctuations.
- Traders can use indicators like Average True Range (ATR) to determine the appropriate position size based on market volatility.
Dollar Risk Method
- The dollar risk method involves determining the amount of money you are willing to risk on a trade based on the distance to your stop-loss level.
- By calculating the difference between your entry price and stop-loss level, you can determine the dollar amount at risk.
- Dividing this dollar amount by the distance to your stop-loss level gives you the position size in lots.
Risk-to-Reward Ratio
The risk-to-reward ratio is a crucial concept in Forex risk management as it helps traders assess the potential profitability of a trade relative to the risk involved. By understanding this ratio, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their overall trading performance.
Significance of Risk-to-Reward Ratio
The risk-to-reward ratio is significant because it allows traders to determine whether a trade is worth taking based on the potential reward compared to the risk. A favorable risk-to-reward ratio indicates that the potential profit is higher than the potential loss, making the trade more attractive.
- Traders aim to find trades with a high risk-to-reward ratio, such as 1:2 or higher, to ensure that they are risking less to potentially gain more.
- By using this ratio, traders can set realistic profit targets and stop-loss levels, helping them manage their risk effectively.
- Having a good risk-to-reward ratio can also improve a trader’s overall trading consistency and long-term profitability.
Examples of Favorable Risk-to-Reward Ratios
- A trade with a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:3 means that for every $1 risked, the potential reward is $3. This indicates a favorable ratio where the potential profit outweighs the risk.
- Another example could be a trade with a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2, where the potential reward is twice the amount of the risk. This also represents a good risk-to-reward ratio.
- Traders often look for trades with a risk-to-reward ratio that aligns with their trading strategy and risk tolerance to maximize profitability.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering Forex risk management strategies is crucial for any trader looking to navigate the unpredictable waters of the foreign exchange market. By implementing these techniques effectively, traders can minimize potential losses and optimize their trading outcomes.