Kicking off with Dollar-cost averaging for stocks, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone for what’s to come. Dollar-cost averaging is a popular strategy that allows investors to spread out their stock purchases over time, reducing the impact of market volatility and potentially lowering the average cost per share. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of this investment method, from its definition to practical implementation.
Definition of Dollar-cost averaging for stocks

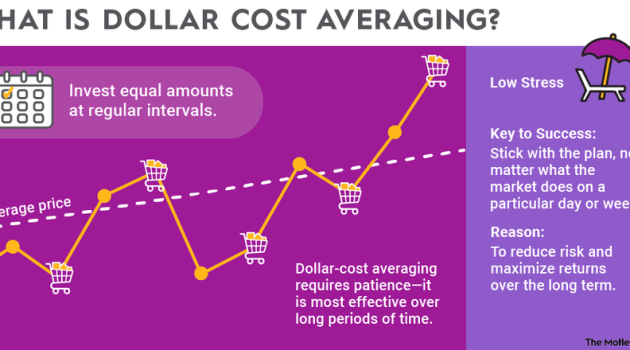
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy used by investors to mitigate the impact of market volatility on their stock investments. Instead of trying to time the market by buying stocks at specific highs or lows, investors using this approach consistently invest a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the stock price.
How Dollar-cost averaging works
- Investors decide on a fixed amount of money to invest in a particular stock or a diversified portfolio.
- They then set up a schedule to make regular investments, such as monthly or quarterly.
- Regardless of whether the stock price is high or low, the investor buys a set number of shares with each investment.
- Over time, this strategy averages out the cost of the shares purchased, reducing the impact of market fluctuations on the overall investment.
Purpose of Dollar-cost averaging in stock investments
- Minimizes the risk of making poor investment decisions based on market timing.
- Helps to smooth out the effects of market volatility on the overall investment.
- Encourages disciplined investing by removing emotional bias from the decision-making process.
Examples of Dollar-cost averaging in action
For example, let’s say an investor decides to invest $500 in a particular stock every month. In one month, the stock price may be $50 per share, resulting in the purchase of 10 shares. The following month, the stock price may drop to $40 per share, allowing the investor to buy 12.5 shares with the same $500. Over time, the average cost per share will be calculated, reducing the impact of market fluctuations on the overall investment.
Benefits of Dollar-cost averaging for stocks

Dollar-cost averaging is a popular investment strategy that offers several benefits for investors looking to build wealth over time. Let’s explore the advantages of using dollar-cost averaging when investing in stocks.
Reducing risk and volatility
Dollar-cost averaging can help reduce the risk and volatility associated with investing in the stock market. By spreading out your investments over time, you are less exposed to the fluctuations in stock prices. This means that you are not as affected by sudden market downturns or spikes, as your investments are averaged out over a period.
Taking advantage of market fluctuations
One of the key benefits of dollar-cost averaging is that it allows investors to take advantage of market fluctuations. When stock prices are low, you automatically buy more shares, and when prices are high, you buy fewer shares. This strategy ensures that you are buying more shares when prices are low, maximizing your returns over the long term.
Consistent investing
Another advantage of dollar-cost averaging is that it promotes consistent investing habits. By investing a set amount of money at regular intervals, you are less likely to try and time the market. This disciplined approach can help you build a diversified portfolio over time, without the stress of trying to predict market movements.
Implementing Dollar-cost averaging for stocks

When it comes to implementing dollar-cost averaging for stocks, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to maximize the benefits of this investment strategy. Below are step-by-step guidelines on how to start, the frequency and amount of investments needed, and tips for choosing suitable stocks.
Getting Started with Dollar-cost Averaging
To start dollar-cost averaging for stock investments, follow these steps:
- Set a budget: Determine how much you can afford to invest regularly.
- Select a brokerage account: Choose a reputable broker that offers the option for automated investments.
- Choose your stocks: Select a diverse range of stocks or ETFs to reduce risk.
- Set up automatic investments: Schedule regular purchases of stocks at fixed intervals, regardless of market conditions.
Frequency and Amount of Investments
For effective dollar-cost averaging, consider investing a consistent amount at regular intervals, such as weekly or monthly. The key is to stick to your investment plan and avoid trying to time the market. By investing the same amount consistently, you benefit from purchasing more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high.
Tips for Choosing Suitable Stocks, Dollar-cost averaging for stocks
When selecting stocks for dollar-cost averaging, consider the following tips:
- Focus on stable companies: Choose stocks of companies with a proven track record of stability and growth.
- Diversify your portfolio: Invest in different sectors to reduce risk and maximize potential returns.
- Consider dividend-paying stocks: Companies that pay dividends can provide a steady income stream, enhancing the overall performance of your portfolio.
- Research and monitor: Stay informed about the companies you invest in and adjust your portfolio as needed based on market conditions.
Comparison with other investment strategies
When comparing dollar-cost averaging with other investment strategies, it is essential to understand the differences in approach, risk management, and potential outcomes. Let’s delve into how dollar-cost averaging stacks up against lump-sum investing and market timing.
Dollar-Cost Averaging vs. Lump-Sum Investing
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Involves regularly investing a fixed amount of money at predetermined intervals, regardless of market conditions. This approach helps mitigate the impact of market volatility by spreading out the investment over time.
- Lump-Sum Investing: Involves investing a large sum of money all at once. This strategy can potentially lead to higher returns if the market performs well immediately after the investment. However, it also exposes the investor to higher risk if the market experiences a downturn shortly after the investment.
Pros and Cons of Dollar-Cost Averaging
- Pros:
- Reduces the impact of market volatility on investment returns.
- Encourages consistent investing habits.
- Can potentially lead to lower average cost per share over time.
- Cons:
- May result in missed opportunities for higher returns during bull markets.
- Does not guarantee protection against market downturns.
- Requires discipline to stick to the investment schedule.
Dollar-Cost Averaging as a Disciplined Approach
Dollar-cost averaging offers a disciplined and systematic approach to stock investing by removing the need to time the market. Instead of trying to predict market movements, investors focus on consistently investing over the long term. This approach helps reduce the emotional impact of market fluctuations and promotes a long-term investment mindset.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Dollar-cost averaging for stocks offers investors a disciplined and strategic approach to building their portfolio. By consistently investing fixed amounts at regular intervals, investors can take advantage of market fluctuations and potentially achieve more stable returns over the long term. Whether you’re a novice or experienced investor, incorporating dollar-cost averaging into your investment strategy can help you navigate the unpredictable waters of the stock market with more confidence.
When it comes to investing in the stock market, there are various types of stocks to consider. From growth stocks that offer high potential returns to value stocks that are undervalued, each type has its own unique characteristics. It’s important for investors to understand the differences between these types of stocks to make informed decisions.
To learn more about the different types of stocks to invest in, check out this comprehensive guide on types of stocks to invest in.
When considering types of stocks to invest in, it’s important to diversify your portfolio to minimize risks. Blue-chip stocks are known for their stability and long track record of success, making them a popular choice for conservative investors. On the other hand, growth stocks offer the potential for high returns but come with higher risks due to their volatile nature.
Penny stocks, although risky, can also be lucrative if chosen wisely. Understanding the different types of stocks available can help you make informed investment decisions. Learn more about types of stocks to invest in to build a strong investment strategy.