Currency pair correlations explained, this introduction delves into the intricate world of forex trading, shedding light on how understanding correlations can enhance risk management strategies and overall trading success.
Exploring major currency pairs, economic indicators, and geopolitical events, this overview sets the stage for a deeper understanding of currency pair correlations.
Overview of Currency Pair Correlations

Currency pair correlations in forex trading refer to the relationship between the price movements of different currency pairs. Understanding these correlations can help traders manage risk more effectively by predicting how one currency pair may move based on the movements of another pair.
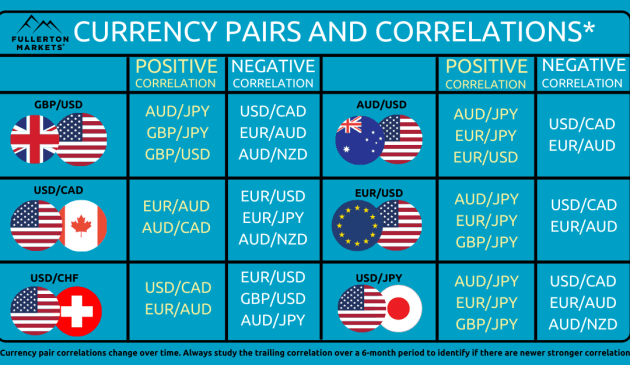
For example, the EUR/USD and USD/CHF are known to have a strong negative correlation. This means that when the EUR/USD pair goes up, the USD/CHF pair tends to go down, and vice versa. On the other hand, the AUD/USD and NZD/USD pairs have a positive correlation, meaning they tend to move in the same direction.
Examples of Major Currency Pairs and Their Correlations
- The EUR/USD and USD/CHF pairs have a strong negative correlation, typically moving in opposite directions.
- The AUD/USD and NZD/USD pairs have a positive correlation, often moving in the same direction.
- The USD/JPY and USD/CAD pairs may have a weaker correlation, with movements that are not as closely aligned.
Understanding Correlations for Risk Management
- By analyzing currency pair correlations, traders can diversify their portfolios by choosing pairs that are not highly correlated, reducing overall risk.
- Correlations can also help traders hedge their positions by taking opposite positions on negatively correlated pairs to offset potential losses.
- Additionally, understanding correlations can provide insights into market sentiment and help traders make more informed trading decisions.
Factors Influencing Currency Pair Correlations
Currency pair correlations are influenced by a variety of factors that can impact the relationship between different pairs. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders and investors to make informed decisions in the forex market.
Economic Indicators:
Economic indicators play a significant role in influencing currency pair correlations. These indicators provide insights into the economic health of a country, affecting the strength of its currency. For example, strong economic data such as GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates can lead to a stronger currency. As a result, currency pairs involving that currency may exhibit positive correlations. On the other hand, weak economic data can lead to a depreciation of the currency, impacting correlations in a negative way.
Geopolitical Events:
Geopolitical events can also have a profound impact on currency pair correlations. Political instability, conflicts, and trade disputes can create uncertainty in the market, leading to fluctuations in currency values. For instance, a geopolitical crisis in a major oil-producing country can cause oil prices to surge, which may in turn affect currencies of countries heavily reliant on oil exports. This can result in correlations between currency pairs with exposure to oil prices.
Overall, traders need to stay informed about economic indicators and geopolitical events to anticipate how currency pair correlations may be influenced. By monitoring these factors closely, traders can better navigate the forex market and make strategic trading decisions.
Types of Currency Pair Correlations

In the forex market, currency pair correlations can be classified into three main types: positive correlation, negative correlation, and no correlation. Each type of correlation indicates the relationship between the movements of two currency pairs.
Positive Correlation
A positive correlation between two currency pairs means that they tend to move in the same direction. When one currency pair strengthens, the other pair also tends to strengthen, and vice versa. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD are known to have a positive correlation, as they both typically move in the same direction.
Negative Correlation, Currency pair correlations explained
Conversely, a negative correlation between two currency pairs indicates that they move in opposite directions. When one currency pair strengthens, the other pair tends to weaken, and vice versa. An example of negative correlation in the forex market is USD/JPY and EUR/USD, where these pairs often move in opposite directions.
No Correlation
When two currency pairs have no correlation, their movements are independent of each other. This means that the movements of one pair do not influence the movements of the other pair. An example of currency pairs with no correlation could be AUD/USD and USD/CHF, as their price movements are not related to each other.
Analyzing Currency Pair Correlations: Currency Pair Correlations Explained
When it comes to analyzing currency pair correlations, traders have several tools at their disposal to make informed decisions. One of the key methods is to use correlation coefficients and correlation matrices to understand the relationships between different currency pairs.
Correlation Coefficients and Correlation Matrices
Correlation coefficients are numerical values that indicate the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two currency pairs. They range from -1 to 1, where:
-1 indicates a perfect negative correlation,
0 indicates no correlation, and
1 indicates a perfect positive correlation.
Correlation matrices, on the other hand, provide a visual representation of the correlation coefficients between multiple currency pairs. By looking at a correlation matrix, traders can quickly identify which pairs are positively correlated, negatively correlated, or not correlated at all.
Interpreting Correlation Data for Trading Decisions
When interpreting correlation data for trading decisions, it is essential to understand that correlations can change over time due to various factors such as economic events, geopolitical developments, or market sentiment shifts. Here are some insights on how to use correlation data effectively:
- Positive Correlations: If two currency pairs have a positive correlation, it means they tend to move in the same direction. Traders can use this information to confirm trends or identify potential trading opportunities.
- Negative Correlations: Conversely, negative correlations indicate that two currency pairs move in opposite directions. Traders can use this information to hedge their positions or diversify their portfolios.
- No Correlations: When two currency pairs have no correlation, it means their movements are independent of each other. Traders can use this information to reduce risk by trading uncorrelated pairs.
Final Summary

In conclusion, Currency pair correlations explained offer valuable insights into the interconnected nature of the forex market, empowering traders to make more informed decisions and navigate the complexities of trading with confidence.
When it comes to forex trading, many traders are drawn to the allure of exotic currency pairs. These pairs involve currencies from smaller or less commonly traded countries, offering unique trading opportunities. While they may have lower liquidity and higher spreads compared to major pairs, they can provide diversification and potential for higher returns.
Traders need to carefully assess the risks and market conditions before delving into exotic pairs, but for those willing to take on the challenge, they can add an exciting dimension to their trading portfolios.
When it comes to forex trading, many traders are familiar with major currency pairs like EUR/USD or USD/JPY. However, experienced traders often venture into the world of exotic currency pairs. These pairs involve currencies from smaller or emerging market economies, offering unique opportunities for diversification and potentially higher returns.
While they may carry higher risks due to lower liquidity and wider spreads, exotic currency pairs can be a valuable addition to a well-rounded trading portfolio.