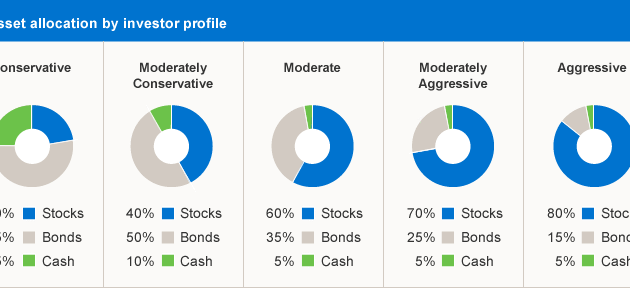
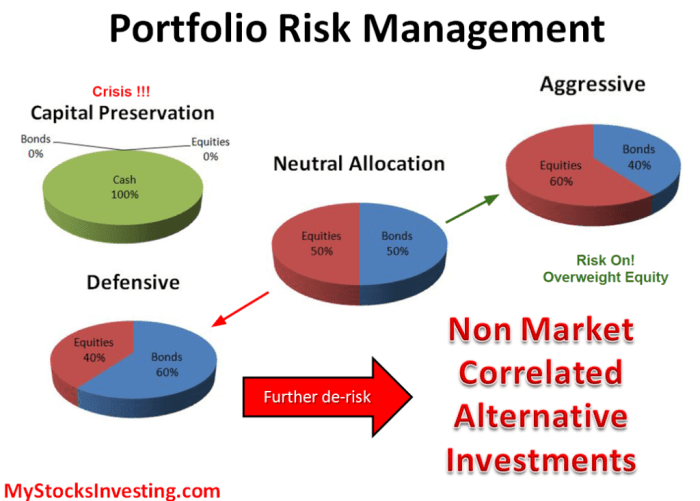
With Asset allocation strategies for stock portfolios at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Understanding the importance of diversification and strategic asset allocation is crucial for investors looking to optimize their stock portfolios. This comprehensive guide delves into various asset allocation strategies, risk management techniques, and the influence of Modern Portfolio Theory on portfolio construction.
Asset Allocation Strategies: Asset Allocation Strategies For Stock Portfolios

Asset allocation is the strategic distribution of an investor’s portfolio among different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, cash, real estate, and commodities. The goal is to optimize returns while managing risk based on the investor’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Asset Classes in Portfolios
Asset classes that investors can include in their portfolios for diversification purposes are:
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for high returns but come with higher risk.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations that provide regular interest payments and lower risk compared to stocks.
- Cash: Includes cash equivalents like money market funds and savings accounts, providing liquidity and stability.
- Real Estate: Investing in physical properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs) for potential rental income and capital appreciation.
- Commodities: Raw materials like gold, oil, or agricultural products that can act as a hedge against inflation or economic uncertainty.
Diversification Importance
Diversification is crucial in asset allocation as it helps reduce overall portfolio risk by spreading investments across different asset classes that do not move in tandem. By including a mix of assets with varying correlations, investors can potentially minimize losses during market downturns and optimize returns over the long term.
Modern Portfolio Theory
Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) is a framework for constructing efficient investment portfolios that aim to maximize returns for a given level of risk. Developed by Harry Markowitz in the 1950s, MPT is based on the premise that investors are rational and seek to optimize their investment decisions.
Principles of Modern Portfolio Theory
- Asset Diversification: MPT emphasizes diversification across different asset classes to reduce risk. By spreading investments across various assets with low correlation, the overall portfolio risk can be minimized.
- Efficient Frontier: MPT helps investors identify the optimal portfolio allocation that offers the highest expected return for a given level of risk. The efficient frontier represents the set of portfolios that provide the best possible returns for a given level of risk.
- Risk-Return Tradeoff: MPT recognizes that there is a direct relationship between risk and return. Investors must balance their willingness to take on risk with their desired level of return when constructing a portfolio.
Influence on Asset Allocation Strategies
Modern Portfolio Theory has a significant impact on asset allocation strategies by guiding investors to build diversified portfolios that offer the highest returns for a given level of risk. By considering the correlation between different assets and their expected returns, investors can optimize their portfolio allocations to achieve their financial goals.
Comparison of Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
- Traditional Approach: Traditional portfolio construction often focused on individual security selection without considering diversification or risk management. This approach may lead to concentrated portfolios with higher levels of risk.
- Modern Approach: In contrast, the modern approach based on MPT emphasizes the importance of diversification and risk management to achieve optimal portfolio allocations. By considering the entire portfolio as a whole, investors can create more efficient and balanced investment strategies.
Risk Management Techniques

Risk management techniques play a crucial role in asset allocation strategies, helping investors mitigate potential losses and protect their portfolios. By understanding different risk management techniques and how they can be applied, investors can make more informed decisions to achieve their financial goals.
Diversification
Diversification is a key risk management technique that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. By diversifying their portfolios, investors can reduce the impact of volatility in any single investment and minimize overall risk. This technique helps to cushion against market fluctuations and unexpected events that may affect specific industries or regions.
Asset Correlation
Asset correlation is another important risk management technique that involves analyzing the relationship between different assets in a portfolio. By investing in assets that are not highly correlated, investors can reduce the risk of losses from a downturn in a specific market or sector. Understanding asset correlation allows investors to build a more resilient portfolio that can withstand market volatility.
Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance refers to an investor’s ability to withstand fluctuations in the value of their investments. It is crucial to consider risk tolerance when making asset allocation decisions, as it determines the level of risk that an investor is comfortable with. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to equities, while those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach with a higher allocation to fixed-income securities.
Hedging Strategies
Hedging strategies involve using financial instruments to offset the risk of potential losses in a portfolio. For example, investors can hedge against market risk by purchasing put options or using futures contracts to protect their downside. Hedging can also be used to mitigate currency risk, interest rate risk, and other specific risks that may impact the value of investments.
Tactical vs. Strategic Asset Allocation

When it comes to managing stock portfolios, investors often employ either tactical or strategic asset allocation strategies. Each approach has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, and understanding the differences between the two can help investors make informed decisions to achieve their financial goals.
Tactical Asset Allocation, Asset allocation strategies for stock portfolios
Tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments to a portfolio based on market conditions or specific opportunities. This approach allows investors to capitalize on short-term market inefficiencies or trends, with the goal of maximizing returns. However, tactical asset allocation requires active monitoring and frequent adjustments, which can increase transaction costs and taxes.
- Benefits of Tactical Asset Allocation:
Tactical asset allocation can help investors take advantage of short-term market opportunities and potentially outperform the market.
- Drawbacks of Tactical Asset Allocation:
Requires constant monitoring and adjustment, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation, on the other hand, involves setting a long-term target allocation for various asset classes based on an investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals. This approach aims to create a diversified portfolio that can weather market fluctuations over time. While strategic asset allocation requires less active management than tactical allocation, it may not fully capture short-term market opportunities.
- Benefits of Strategic Asset Allocation:
Provides a disciplined approach to investing and helps investors stay focused on long-term goals.
- Drawbacks of Strategic Asset Allocation:
May miss out on short-term market trends or opportunities for higher returns.
Real-World Examples
One example of successful tactical asset allocation is George Soros’ Quantum Fund, which famously capitalized on market trends and macroeconomic events to generate high returns. On the other hand, the Yale Endowment Fund is known for its strategic asset allocation approach, focusing on long-term diversification and risk management to achieve consistent returns.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, mastering asset allocation strategies for stock portfolios is key to achieving long-term financial success. By implementing a combination of tactical and strategic approaches, investors can navigate market fluctuations and mitigate risks effectively. Dive into the world of asset allocation strategies and elevate your investment game today.
When it comes to stock analysis, understanding how to use the P/E ratio is crucial. The P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, is a key metric used by investors to evaluate a company’s stock. By comparing the stock price to the company’s earnings per share, investors can determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued.
To learn more about how to use the P/E ratio in stock analysis, check out this informative guide on How to use the P/E ratio in stock analysis.
When it comes to stock analysis, understanding the P/E ratio is crucial. The P/E ratio, or price-to-earnings ratio, is a key metric used by investors to evaluate a company’s financial health and determine if a stock is overvalued or undervalued.
By comparing the stock price to the company’s earnings per share, investors can gain insight into how the market values the company. To learn more about how to use the P/E ratio in stock analysis, check out this informative article.