Exploring the intricacies of How to use the P/E ratio in stock analysis, this introduction sets the stage for a deep dive into the world of stock evaluation.
Detailing the importance of understanding the P/E ratio and how it can impact investment decisions, this guide aims to demystify the complexities of financial analysis for investors of all levels.
Understanding the P/E Ratio: How To Use The P/E Ratio In Stock Analysis

The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is a fundamental metric used in stock analysis to evaluate a company’s valuation in relation to its earnings. It is calculated by dividing the current market price per share by the earnings per share (EPS). This ratio provides investors with insights into how much they are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings generated by the company.
Significance of the P/E Ratio for Investors
- The P/E ratio helps investors gauge whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly priced. A high P/E ratio may indicate that the stock is overvalued, while a low P/E ratio could suggest undervaluation.
- Investors can use the P/E ratio to compare different companies within the same industry or sector. This comparison allows investors to identify potentially lucrative investment opportunities.
- By analyzing the trend of a company’s P/E ratio over time, investors can assess the stock’s growth prospects and market sentiment towards the company.
Comparison to Other Financial Ratios
- While the P/E ratio is a popular valuation metric, investors should not rely solely on this ratio for decision-making. It is essential to consider other financial ratios, such as the Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio, Return on Equity (ROE), and Debt-to-Equity ratio, to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial health.
- Each financial ratio offers unique insights into different aspects of a company’s performance and should be used in conjunction with the P/E ratio to make informed investment decisions.
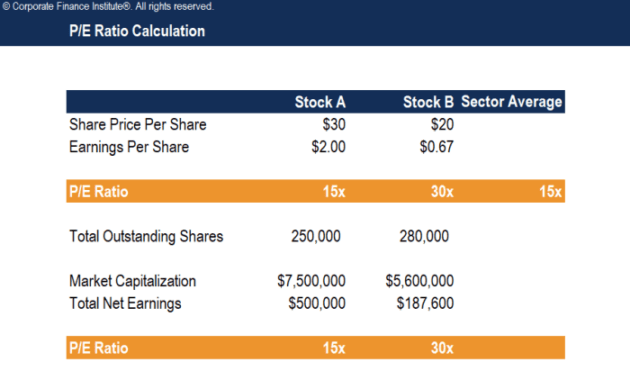
Calculating the P/E Ratio
When it comes to evaluating a stock, the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is a key metric that investors use to gauge the valuation of a company. Calculating the P/E ratio involves a simple formula that provides insights into how the market values a stock relative to its earnings.
Formula for Calculating the P/E Ratio
To calculate the P/E ratio, you can use the following formula:
P/E Ratio = Price per Share / Earnings per Share
Determining the P/E Ratio
- Step 1: Determine the Price per Share – This is the current market price of a single share of the stock.
- Step 2: Calculate the Earnings per Share – This is the net income of the company divided by the total number of outstanding shares.
- Step 3: Plug the values into the formula – Divide the Price per Share by the Earnings per Share to get the P/E ratio.
Examples of Calculating the P/E Ratio
Let’s consider an example using real stock data:
- Price per Share: $50
- Earnings per Share: $5
Calculating the P/E ratio:
P/E Ratio = $50 / $5 = 10
In this example, the P/E ratio for the stock would be 10, indicating that investors are willing to pay 10 times the company’s earnings for each share. This can provide valuable insights into the stock’s valuation and potential investment opportunities.
Interpreting the P/E Ratio
When it comes to analyzing stocks, understanding how to interpret the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is crucial. The P/E ratio can provide insights into market expectations and the valuation of a company’s stock.
A high P/E ratio typically indicates that investors are willing to pay more for the company’s earnings, suggesting that the stock may be overvalued. On the other hand, a low P/E ratio may signal that the stock is undervalued, as investors are paying less for each dollar of earnings.
Factors Influencing Fluctuations in the P/E Ratio
- Economic Conditions: Changes in the overall economy can impact a company’s earnings and subsequently affect its P/E ratio.
- Market Sentiment: Investor sentiment and market trends can also influence the P/E ratio, leading to fluctuations.
- Company Performance: Strong or weak financial performance of a company can directly impact its P/E ratio.
Scenarios for a High P/E Ratio
- High-Growth Companies: Companies with high growth potential often have high P/E ratios as investors expect significant earnings growth in the future.
- Industry Leaders: Established companies with a dominant market position may justify a high P/E ratio due to their stability and potential for continued success.
Concerns with a High P/E Ratio
- Speculative Bubble: A significantly high P/E ratio could indicate a speculative bubble, where the stock price is inflated beyond its intrinsic value.
- Earnings Volatility: Companies with erratic earnings may have a high P/E ratio that is not sustainable in the long run.
Using the P/E Ratio for Investment Decisions

When it comes to making investment decisions, the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio can be a valuable tool for investors to assess the valuation of a stock. By understanding how to interpret the P/E ratio, investors can identify potential opportunities and risks in the market.
Identifying Undervalued or Overvalued Stocks
One way to use the P/E ratio is to compare it to the average P/E ratio of similar companies in the same industry. If a stock has a lower P/E ratio than its peers, it may indicate that the stock is undervalued. On the other hand, a higher P/E ratio could suggest that the stock is overvalued relative to its industry.
Limitations of Relying Solely on the P/E Ratio, How to use the P/E ratio in stock analysis
While the P/E ratio is a useful metric, it should not be the sole factor in making investment decisions. The ratio does not take into account other important factors such as growth prospects, competitive landscape, and overall market conditions. Therefore, relying solely on the P/E ratio may lead to overlooking crucial information that could impact the stock’s performance.
Incorporating the P/E Ratio into Stock Analysis Strategy
Investors can incorporate the P/E ratio into their overall stock analysis strategy by using it in conjunction with other financial metrics and qualitative factors. By combining the P/E ratio with factors such as earnings growth, dividend yield, and market trends, investors can gain a more comprehensive view of a stock’s valuation and potential for growth.
Closure

In conclusion, mastering the art of utilizing the P/E ratio in stock analysis can provide valuable insights for investors looking to make informed decisions in the dynamic world of finance.
When it comes to navigating the stock market as a beginner, it’s essential to have a solid strategy in place. One of the best stock market strategies for beginners is to start with thorough research and education. Understanding the basics of investing, learning how to analyze market trends, and setting realistic goals are key components of a successful approach.
Additionally, diversifying your portfolio and staying updated on market news can help minimize risks and maximize returns. By following these strategies, beginners can build a strong foundation for long-term financial growth.
When diving into the world of stock market investing, beginners may feel overwhelmed by the vast amount of information available. It’s crucial to have a solid strategy in place to navigate the market effectively. Understanding the best stock market strategies for beginners can help mitigate risks and maximize returns.
Whether it’s diversifying your portfolio, conducting thorough research, or setting realistic goals, having a well-defined strategy is key to success. Check out this comprehensive guide on best stock market strategies for beginners to kickstart your investment journey.