Delving into Using moving averages for trading, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with a focus on practical applications for traders looking to maximize their profits and minimize risks. Exploring the intricacies of moving averages and their impact on trading decisions, this guide offers valuable insights for both novice and experienced traders alike.
Understanding the key concepts and strategies behind using moving averages can significantly improve your trading performance and help you navigate the complexities of the financial markets with confidence.
Overview of Moving Averages

Moving averages are a popular technical analysis tool used by traders to identify trends and potential entry or exit points in the market. They smooth out price data over a specified period, providing a clearer picture of the overall trend.
There are several types of moving averages commonly used by traders, including simple moving averages (SMA), exponential moving averages (EMA), and weighted moving averages (WMA). Each type has its own characteristics and is used based on the trader’s preference and trading strategy.
Types of Moving Averages
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): This type calculates the average price of a security over a specific number of periods. It gives equal weight to each data point in the calculation.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to current price movements compared to SMA.
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA): WMA assigns more weight to recent data points, similar to EMA, but allows traders to customize the weighting scheme.
Significance of Moving Averages in Trading, Using moving averages for trading
Moving averages are essential tools in technical analysis as they help traders identify trends, support, and resistance levels, as well as potential reversal points. They can also be used to generate trading signals, such as moving average crossovers, where the shorter-term moving average crosses above or below the longer-term moving average.
Types of Moving Averages

Moving averages are a popular tool used in technical analysis to smooth out price data and identify trends. There are several types of moving averages, each with its own characteristics and applications.
Simple Moving Averages (SMA) vs. Exponential Moving Averages (EMA)
Simple moving averages (SMA) calculate the average price over a specific number of periods equally. This means that each data point in the calculation has the same weight. On the other hand, exponential moving averages (EMA) give more weight to recent prices, making them more responsive to price changes. EMAs react faster to price movements compared to SMAs.
Weighted Moving Averages
Weighted moving averages assign different weights to each data point in the calculation. This means that certain data points have more influence on the average than others. Weighted moving averages are more sensitive to price changes compared to SMAs but less responsive than EMAs.
Pros and Cons of Different Moving Averages
– SMAs are easy to calculate and provide a smooth average of prices over a specific period. However, they may lag behind price movements.
– EMAs react quickly to price changes, making them ideal for short-term trading strategies. However, they can be more volatile and prone to false signals.
– Weighted moving averages offer a balance between SMAs and EMAs, providing a smoother average while still being responsive to price changes. However, determining the appropriate weights can be subjective and may vary depending on the trader’s preferences.
Overall, the choice between different types of moving averages depends on the trader’s trading style, timeframe, and risk tolerance.
Setting Up Moving Averages
When it comes to setting up moving averages for trading, traders need to carefully determine the appropriate time periods for their moving averages. This decision is crucial as it can significantly impact the effectiveness of this technical analysis tool. Traders typically consider factors such as their trading strategy, the timeframe they are trading in, and the level of market volatility.
Determining Time Periods
- Short-term traders often use shorter time periods, such as 9 or 20 days, to capture more immediate price movements.
- Longer-term investors may opt for longer time periods, like 50 or 200 days, to filter out short-term noise and focus on broader trends.
- Experimenting with different time periods and observing their impact on historical price data can help traders find the optimal settings for their moving averages.
Setting Up on Trading Platforms
- Most trading platforms offer the ability to add moving averages to price charts. Traders can usually select the type of moving average (simple, exponential, etc.) and input the desired time periods.
- It is essential to customize the moving averages based on individual preferences and trading styles to ensure they align with the trader’s strategy.
Adjusting for Market Volatility
- During periods of high market volatility, it may be beneficial to adjust the time periods of moving averages to capture more significant price swings.
- Traders can experiment with shorter time periods during volatile market conditions to avoid lagging indicators and adapt to rapid price changes.
- Regularly reassessing and fine-tuning moving averages based on market conditions can help traders stay ahead of potential trend reversals.
Using Moving Averages for Trading Signals
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_to_Use_a_Moving_Average_to_Buy_Stocks_Jun_2020-02-85609403fbee41089d13a9ffa649bdac.jpg?w=700)
When it comes to using moving averages for trading signals, they play a crucial role in helping traders identify potential buy or sell opportunities in the market. By analyzing the relationship between different moving averages, traders can make informed decisions on when to enter or exit trades.
Crossovers and Trading Strategies
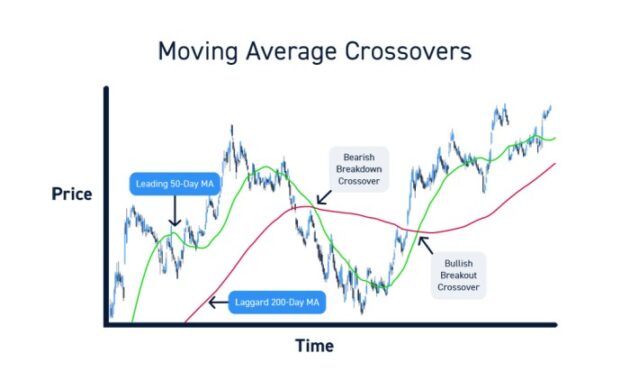
One common way that moving averages generate signals is through crossovers. This occurs when a short-term moving average crosses above or below a long-term moving average. A bullish crossover, where the short-term MA crosses above the long-term MA, signals a potential buy opportunity. Conversely, a bearish crossover, where the short-term MA crosses below the long-term MA, indicates a possible sell signal.
- Example: If a 50-day moving average crosses above a 200-day moving average, it could be interpreted as a bullish signal, suggesting that the price may continue to rise. On the other hand, if the 50-day MA crosses below the 200-day MA, it could indicate a bearish signal, hinting at a potential downtrend.
Interpreting Moving Average Signals
Traders use moving average signals in different market conditions to gauge the momentum and direction of price movements. In an uptrend, traders look for buy signals when the price is above the moving averages, indicating a potential continuation of the upward trend. Conversely, in a downtrend, sell signals are sought when the price is below the moving averages, signaling a possible downward trajectory.
- Example: During a ranging market, where the price moves sideways within a certain range, traders may use moving averages to identify potential entry and exit points based on support and resistance levels. A crossover within the range could signal a shift in momentum, prompting traders to adjust their positions accordingly.
End of Discussion: Using Moving Averages For Trading
In conclusion, incorporating moving averages into your trading toolkit can provide you with a strategic advantage in identifying potential trends and making informed decisions. By mastering the art of utilizing moving averages effectively, traders can enhance their overall trading success and achieve their financial goals with greater precision.
When it comes to forex trading, choosing the best currency pair is crucial for your success. Factors to consider include volatility, liquidity, and correlation. To make an informed decision, conduct thorough research and analysis. Learn more about how to choose the best currency pair to maximize your profits and minimize risks.
When it comes to trading in the forex market, choosing the best currency pair is crucial for your success. Factors like volatility, liquidity, and correlation should be considered. To learn more about how to choose the best currency pair, check out this comprehensive guide on How to choose the best currency pair.